Keywords: Vehicle Network information security, Internet of Vehicle, Cloud
Hsin-Te Wu
Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering, National Penghu University of Science and Technology, Penghu, Taiwan
This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
Abstract
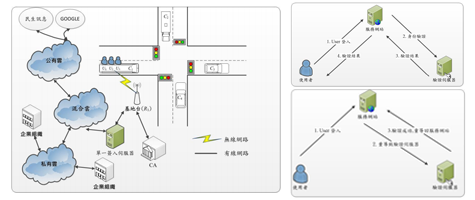
This paper is mainly to design a cloud security mechanism for cloud applications in VANETs. At present, cloud computing is one of the key points for the government to promote industrial development. In this paper, we divide the cloud into public clouds, private clouds and hybrid clouds. Vehicles or passengers can use public ownership. Cloud access to road conditions or mass transit information, private cloud part of the mass transit can access the current driving record, users can access the relevant information of the enterprise, hybrid cloud is the combination of public cloud and private cloud, whether in the cloud computing or VANETs All need cyber and information security protection. At present, many VANETs security research only deals with information communication. There is no information storage part. The cloud computing security research only focuses on information protection, and does not target user privacy and anonymity. This paper designs a network. It is confidential, certified, undeniable, conditional, and untrackable. This article mainly needs to achieve 1. Identity verification mechanism, passengers and vehicles can verify each other's identity, and can be verified with a single check-in, 2. Keep the vehicle or user's privacy and anonymity, need to be able to change vehicles or use Anonymous ID and related parameters, 3. Private communication mechanism, any vehicle or user can conduct private communication, 4. Information security encryption method, allowing data to keep ciphertext on the cloud server, avoiding internal personnel or hackers Capture data.
References
- U.S. Dept. Transp., ” Nat. Highway Traffic Safety Admin.”, Vehicle Safety Communications Project. 2006.
- S. Lee, G. Pan, J. Park, M. Gerla, and S. Lu, ” Secure incentives for commercial ad dissemination in vehicular networks”, in Proc. ACM IntSymp. MobiHoc ,pp. 150-159, 2007. Google Scholar
- IEEE Trial-Use Standard for Wireless Access in Vehicular Environments (WAVE) – Networking Services.IEEE 1609, 2006.
- IEEE P802.11p/D11.0, “Draft Amendment for Wireless Access in Vehicular Environments (WAVE),” IEEE 802.11 Working Group of the IEEE 802 Committee, Mar. 2010.
- Qing Wang, Supeng Leng, Huirong Fu, and Yan Zhang, “An IEEE 802.11p-Based Multichannel MAC Scheme With Channel Coordination for Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks”, IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, VOL. 13, NO. 2, JUNE 2012. Google Scholar
- Lo-Yao Yeh and Jiun-Long Huang, “PBS: A Portable Billing Scheme with Fine-Grained Access Control for Service-Oriented Vehicular Networks”, IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, Vol. 13, No. 11, November 2014. Google Scholar
- Ming-Chin Chuang and Jeng-Farn Lee, “TEAM: Trust-Extended Authentication Mechanism for Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks” , IEEE Systems Journal, Vol. 8, No. 3, September 2014. Google Scholar
- S. Biswas and J. Misic, “A cross-layer approach to privacypreserving authentication in WAVE-enabled VANETs,” IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, vol. 62, no. 5, pp. 2182– 2192, 2013. Google Scholar
- S.-J.Horng, S.-F. Tzeng, Y. Pan et al., “B-SPECS+: batch verification for secure pseudonymous authentication in VANET,” IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, vol. 8, no. 11, pp. 1860–1875, 2013. Google Scholar
- Song Guo, Deze Zeng and Yang Xiang, “Chameleon Hashing for Secure and PrivacyPreserving Vehicular Communications”, IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, Vol. 25, No. 11, November 2014. Google Scholar
- T. W. Chim, S. M. Yiu, L. C. K. Hui, and V. O. K. Li, “VSPN: VANET-based secure and privacy-preserving navigation,” IEEE Transactions on Computers, vol. 63, no. 2, pp. 510– 524, 2014. Google Scholar
- Xiaoyan Zhu, Shunrong Jiang, Liangmin Wang, and Hui Li, “Efficient Privacy-Preserving Authentication for Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks”, IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, Vol. 63, No. 2, February 2014. Google Scholar
- Cong Wang, Sherman S.M. Chow, Qian Wang, Kui Ren and Wenjing Lou, “Privacy-Preserving Public Auditing for Secure Cloud Storage”, IEEE Transactions on Computers, Vol. 62, No. 2, FEBRUARY 2013. Google Scholar
- Hong Liu, Huansheng Ning, Qingxu Xiong and Laurence T. Yang, “Shared Authority Based Privacy-Preserving Authentication Protocol in Cloud Computing”, IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, Vol. 26, No. 1, JANUARY 2015. Google Scholar
- J. Zhang,W. Zhen, and M. Xu, “An efficient privacy-preserving authentication protocol in VANETs,” in Proceedings of the 9th IEEE International Conference on Mobile Ad-Hoc and Sensor Networks (MSN ’13), pp. 272–277, December 2013. Google Scholar
- Zahir Tari,” Security and Privacy in Cloud Computing”, IEEE Cloud Computing Published By The IEEE Computer Society 2014. Google Scholar
- YANG Pan, GUI Xiaolin, AN Jian, YAO Jing, LIN Jiancai and TIAN Feng, “A Retrievable Data Perturbation Method Used in Privacy-Preserving in Cloud Computing”, Communications System Design 2014. Google Scholar
- Vijay Varadharajan, and Udaya Tupakula, “Security as a Service Model for Cloud Environment”, IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management, Vol. 11, No. 1, March 2014. Google Scholar
- Jiafu Wan, Daqiang Zhang, Shengjie Zhao, Laurence T. Yang, and Jaime Lloret, “ContextAware Vehicular Cyber-Physical Systems with Cloud Support: Architecture, Challenges, and Solutions”, Context-Aware Networking and Communications 2014. Google Scholar
- M. Scott, “Computing the tate pairing,” in Proceedings of the International Conference on Topics in Cryptology, pp. 293–304, Springer, San Francisco, Calif, USA, 2005. Google Scholar
- D. Boneh and M. K. Franklin, “Identity-based encryption from the weil pairing,” in Proceedings of the 21st Annual International Cryptology Conference on Advances in Cryptology, Santa Barbara, Calif, USA, August 2001.Google Scholar
For more information about this article, please contact us here