Kuo-Hsiung Lee Natural Products Laboratory, School of Pharmacy,Natural Products Laboratory, School of Pharmacy,University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill,Chapel Hill, NC, USA 27599-7360
Download Citation:
|
Download PDF
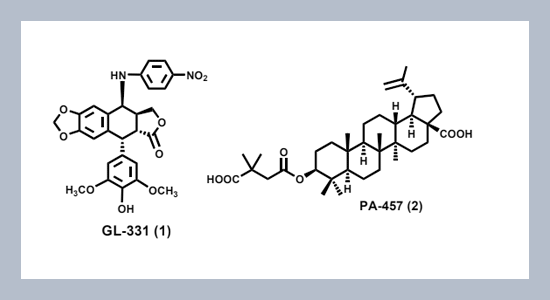
Plants have long served as traditional herbal medicines, and natural products makePlants have long served as traditional herbal medicines, and natural products makeexcellent leads for new drug development. New plant-derived medicines can come from threesources: single active principles, active fractions, and validated prescriptions. Conventionally,for single active compounds, lead discovery and drug development involve highly efficient bioactivity-directed fractionation and isolation (BDFI) coupled with structural characterization,analog synthesis, and mechanism of action studies. Today, new scientific technologies, includingtissue culture and biological screening methods, continue to improve this process. Formulti-component herbal prescriptions, standardization and quality control, including GAP (GoodAgricultural Practice), GMP (Good Manufacturing Practice) and GCP (Good Clinical Practice),must be performed to guarantee high quality and consistency. In addition, reliable chemical,pharmacological, as well as drug administration, distribution, metabolism, excretion, and toxicological(ADMET) studies are needed to validate herbal efficacy and safety. This talk willdiscuss the principles listed above, particularly focusing on the successful development of anticancerand anti-HIV clinical trials candidates from numerous bioactive compounds discovered inthe author’s Natural Products Laboratory. Continued exploration of under-investigated plantspecies should guarantee bright prospects for sustained discovery and development of newmedicines for this century.ABSTRACT
Keywords:
chemotherapeutic agents; plant-derived bioactive compounds; antitumor agents; anti-HIV agents.
Share this article with your colleagues
[1] Wedge, D.-E. and Camper, N. D. 2000.“Connections between agrochemical and“Connections between agrochemical andpharmaceuticals”. Biologically ActiveNatural Products: Pharmaceuticals.CRC Press. Florida. U.S.A.REFERENCES
[2] Balandrin, M.-F., Kinghorn, D.-A. andFarnsworth, N.-R. 1993. “Human MedicinalAgents from Plants”. AmericanChemical Society, Washington D.C.U.S.A.
[3] Lee, K.-H. 2000. Research and futuretrends in the pharmaceutical developmentof medicinal herbs from Chinesemedicine. Public Health Nutrition, 3:515-522.
[4] Lee, K.-H. 2004. Antitumor agents 231and anti-AIDS agents 59. Current developmentsin the discovery and designof new drug candidates from plant naturalproduct leads. Journal of NaturalProducts, 67: 273-283.
[5] Wang, Z.-W., Kuo, Y.-H., Schnur, D.,Bowen, J.-P., Liu, S.-Y., Han, F.-S.,Chang, J.-Y., Cheng, Y.-C. and Lee,K.-H. 1990. Antitumor agents. 113. New4-arylamino derivatives of4'-O-demethylepipodophyllotoxin andrelated compounds as potent inhibitorsof human DNA topoisomerase II. Journalof Medicinal Chemistry, 33:2660-2666.
[6] Liu, S.-Y., Soikes, R., Chen, J., Lee, T.,Taylor, G., Hwang, K.-M. and Cheng,Y.-C. 1993. Presented at 84th AACRAnnual Conference, Orlando, FL, May19-22, University of Texas MD AndersonCancer Center and Chen, J.,Genelabs Technologies, Inc. (personalcommunications).
[7] Xiao, Z., Xiao, Y.-D., Feng, J., Golbraikh,A., Tropsha, A. and Lee, K.-H.2002. Antitumor agents. 213. Modelingof epipodophyllotoxin derivatives usingvariable selection k nearest neighborQSAR method. Journal of MedicinalChemistry, 45: 2294-2309.
[8] Xiao, Z., Bastow, K.-F.; Vance, J.-R. andLee, K.-H. 2004. Antitumor agents. Part227: Studies on novel4'-O-demethyl-epipodophyllotoxins asantitumor agents targeting topoisomeraseII. Bioorganic and MedicinalChemistry, 12: 3339-3344.
[9] Kashiwada, Y., Hashimoto, F.,Cosentino, L.-M., Chen, C.-H., Garrett,P.-E. and Lee, K.-H. 1996. Betulinicacid and dihydrobetulinic acid derivativesas potent anti-HIV agents. Journalof Medicinal Chemistry, 39: 1016-1017.
[10] Li, F., Goila-Gau, R., Salzwedel, K.,Kilgore, N.-R., Reddick, M., Metallana,C., Castillo, A., Zoumplis, D., Martin,D.-E., Orenstein, J.-M., Allaway, G.-P.,Freed, E.-O. and Wild, C.-T. 2003.PA-457: a potent anti-HIV inhibitor thatdisrupts core condensation by targetinga late step in Gag processing. ProceedingsNational Academy Sciences,U.S.A., 100: 13555-13560.
[11] Yu, D., Wild, C.-T., Martin, D.-E., Morris-Natschke, S.-L., Chen, C.-H., Allaway,G.-P. and Lee, K.-H. 2005. Thediscovery of a class of novel HIV-1maturation inhibitors and their potentialin the therapy of HIV. Expert Opinionon Investigational Drugs, 14: 681-693.
[12] Nalawade, S.-M., Sagare, A. -P., Lee,C.-Y., Lao, C.-L. and Tsay, H.-S. 2003.Studies on tissue culture of Chinese medicinalplant resources in Taiwan, theirsustainable utilization. Botanical Bulletinof Academia Sinica, 44: 79-98.
[13] Nicholson, J.-K., Connelly, J., Lindon,J.-C. and Holmes, E. 2002. Metabonomics:a platform for studyingdrug toxicity and gene function. NatureReviews/Drug Discovery, 1:153-161.
ARTICLE INFORMATION
Accepted:
2005-12-04
Available Online:
2005-12-13
Lee, K.-H., 2005. Recent Advances in the Discovery and Development ofRecent Advances in the Discovery and Development ofPlant-derived Chemotherapeutic Agents.International Journal of Applied Science and Engineering, 3, https://doi.org/10.6703/IJASE.2005.3(3).151
Cite this article: