C. C. Cheng1 Dept. of Electrical Engineering, Hsiuping Institute of Technology, Da-Li, Taichung
Download Citation:
|
Download PDF
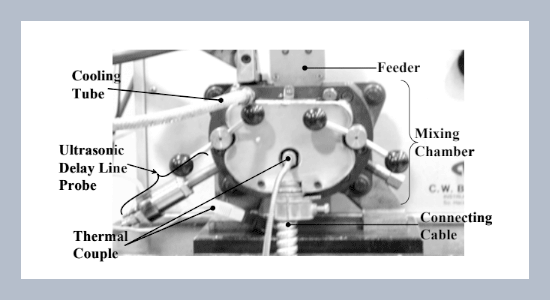
Mixing process in the internal mixer has been monitored by ultrasonic technology real-time, non-intrusively and non-destructively. Visual observation, mechanical torque measurement, and ultrasonic signatures, such as amplitude of transmission and reflection echoes, were used for the diagnosis of the melting process of low density polyethylene (LDPE) and the mixing process of the melted LDPE with a calcium carbonate (CaCO3) powder. Phenomena during the melting and mixing processes, including phase change from solid to melt, and distributing progress of CaCO3 powder were successfully monitored by ultrasound. The ultrasonic signature was able to determine when the polymer had melted thoroughly and mixed with CaCO3 powder completely. The presented ultrasonic technique can be utilized to optimize the melting and mixing processes.ABSTRACT
Keywords:
Mixing condition; internal mixer; ultrasound.
Share this article with your colleagues
REFERENCES
ARTICLE INFORMATION
Accepted:
2009-02-19
Available Online:
2009-02-01
Cheng, C.C. 2009. Mixing conditions of polymer and ceramic powder determined by ultrasound. International Journal of Applied Science and Engineering, 6, 239–244.https://doi.org/10.6703/IJASE.2009.6(3).239
Cite this article: