Chow-Feng Chiang, Hsi-Hsien Yang*, and Tze-Wen Chi Department of Environmental Engineering and Management,Chaoyang University of Technology, Wufeng, Taichung county 413, Taiwan, R.O.C.
Download Citation:
|
Download PDF
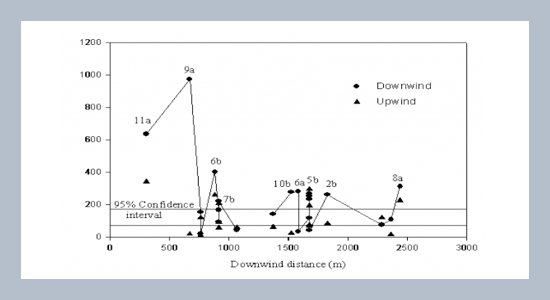
This paper presents results of one-year monitoring of bioaerosol dispersion from a full-scale sludge composting facility in the east coast of the USA. By using two-stage Andersen air samplers with a sequential sampling procedure developed in this study, a total of 24 sets of bioaerosol samples were collected on petri dishes for plate counting. The sampling program utilized a computer air dispersion model (ISCST) to predict the downwind distance at the maximum concentration. Field samplings were performed at upwind, onsite, and predicted downwind locations. The results of this study conclude that the 95% confidence intervals estimated for the background concentrations were: 75-173 cfu/m3 for aerobic bacteria, 262-706 cfu/m3 for mesophilic fungi, 5.0-14 cfu/m3 for thermophilic fungi, and 2.3-12 cfu/m3 for Aspergillus fumigatus. The maximum probably downwind concentrations were evidently increased for aerobic bacteria and thermophilic fungi, but not for mesophilic fungi, fecal coliform, and fecal streptococcus. The zone of influence was estimated to be in the range of 1500-1800 m from the composting facility. Particles smaller than 8 μm constituted 40% of aerobic bacteria and 70-75% of fungi, which may be inhaled into the lung and cause the hypersensitive effect in the respiration system.ABSTRACT
Keywords:
bioaerosol; compost; air dispersion model; Aspergillus fumigatus.
Share this article with your colleagues
[1] Clark, C. S., Rylander, R., and Larsson, L. 1983. Levels of Gram-Negative bacteria, Aspergillus Fumigatus, dust and endotoxin at compost plants. Applied Environmental Microbiology, 45: 1501 -1505.REFERENCES
[2] Kothary, C. L. and Chase, Jr. T. 1984. Levels of Aspergillus Fumigatus in air and in compost at a sewage sludge composting site. Environmental Pollution Series A, 34: 1-14.
[3] Ryland, R. B. 1993. Bronchial reactivity among cotton workers in relation to dust and endotoxin exposure. The Annals of Occupational Hygiene, 37, 1: 57-63.
[4] Zuskin, E., Zagar, Z., Schachter, E. N., Mustajbegovic, J., and Kern, J. 1992. Respiratory symptoms and ventilatory capacity in swine confinement workers. British Journal of Industrial Medicine, 49: 435-440.
[5] Zejda, J. E., Barber, E., Dosman, J. A., Olenchock, S. A., McDuffie, H. H., Rhodes, C., and Hurst, T. 1994. Respiratory health status in swine producers relates to endotoxin exposure in the presence of low dust levels. Journal of Occupational Environment Medicine, 36, 1: 49-56.
[6] Malmberg, P. 1990. Health effects of organic dust exposure in dairy farmers. American Industrial Hygiene Association Journal, 17: 7-15.
[7] Kullman, G. J., Thorne, P. S., Waldron, P. F., Marx, J. J., Ault, B., Lewis, D. M., Siegel, P. D., Olenchock, S. A., and Merchant, J. A. 1998. Organic dust exposure from work in dairy barns. American Industrial Hygiene Association Journal, 59: 403-413.
[8] Eduard, W. and Heederik, D. 1998. Methods for quantitative assessment of airborne levels of noninfectious microorganisms in highly contaminated work environments. American Industrial Hygiene Association Journal, 59: 113-127.
[9] Beffa, T., Blanc, M., Lyon, P. F., Vogt, G., Marchiani, M., Fischer, J. L., and Aragno, M. 1996. Isolation of Thermus Strains from hot composts (60 to 80℃). Applied Environmental Microbiology, 62: 1723- 1727.
[10] Fischer, J. L., Beffa, T., Lyon, P. F., and Aragno, M. 1998. Aspergillus fumigatus in windrow composting: Effect of turning frequency. Waste and Management Research, 16, 4: 320-329.
[11] Haines, J. 1995. Aspergillus in Compost: Straw Man or Fatal Flaw? BioCycle, 36: 32-35.
[12] Jones, B. L. and Cookson, J. T. 1983. Natural atmospheric microbial conditions in a typical suburban area. Applied Environmental Microbiology, 45, 3: 919-934.
ARTICLE INFORMATION
Accepted:
2003-07-22
Available Online:
2003-09-01
Chiang, C.-F., Yang, H.-H.,Chi, T.-W. 2003. Monitoring of bioaerosol emission from a sludge composting facility, International Journal of Applied Science and Engineering, 1, 148–159. https://doi.org/10.6703/IJASE.2003.1(2).148
Cite this article: