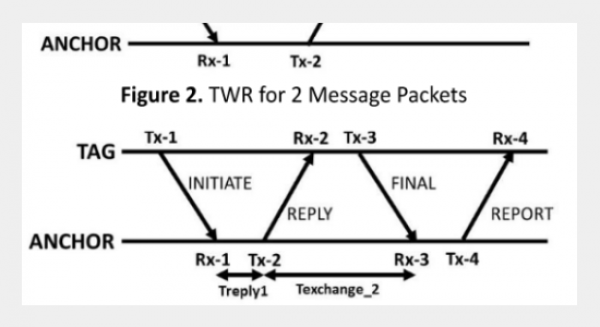
REFERENCES
- [1] C.-C. Wang, C.-L. Chen, and H.-T. Yau, "Bifurcation and Chaotic Analysis of Aeroelastic Systems," J. Comput. Nonlinear Dyn., vol. 9, no. 2, pp. 021004, avr. 2014. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4025124
- [2] C.-T. Hsieh, H.-T. Yau, and C.-C. Wang, "Control circuit design and chaos analysis in an ultrasonic machining system," Eng. Comput., vol. 34, no. 7, pp. 2189‑2211, oct. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1108/EC-02-2017-0044
- [3] C.-T. Hsieh, H.-T. Yau, C.-C. Wang, and Y.-S. Hsieh, "Particle swarm optimization used with proportional-derivative control to analyze nonlinear behavior in the atomic force microscope," Adv. Mech. Eng., vol. 8, no. 9, pp. 1-10, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1177/1687814016667271
- [4] C.-J. Lin, W.-L. Chu, C.-C. Wang, C.-K. Chen, and I.-T. Chen, "Diagnosis of ball-bearing faults using support vector machine based on the artificial fish-swarm algorithm," J. Low Freq. Noise Vib. Act. Control, pp. 1-14, juill. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1177/1461348419861822
- [5] H.-T. Yau, C.-C. Wang, J.-Y. Chang, and X.-Y. Su, "A Study on the Application of Synchronized Chaotic Systems of Different Fractional Orders for Cutting Tool Wear Diagnosis and Identification," IEEE Access, vol. 7, pp. 15903‑15911, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2894815
- [6] B.-L. Jian, C.-C. Wang, J.-Y. Chang, X.-Y. Su, and H.-T. Yau, "Machine Tool Chatter Identification Based on Dynamic Errors of Different Self-Synchronized Chaotic Systems of Various Fractional Orders," IEEE Access, vol. 7, pp. 67278‑67286, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2917094
- [7] T. E. Mezyani, "Méthodologie de surveillance des systèmes dynamiques hybrides," PhD Thesis, Lille 1, 2005.
- [8] R. Isermann, "Estimation of physical parameters for dynamic processes with application to an industrial robot," in proceeding of 6th Mediterranean Electrotechnical Conference, 1991, pp. 12‑17 vol.1. https://doi.org/10.1109/MELCON.1991.161769
- [9] R. J. Patton and J. Chen, "A Review of Parity Space Approaches to Fault Diagnosis," IFAC Proc. Vol., vol. 24, no. 6, pp. 65‑81, sep. 1991. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-6670(17)51124-6
- [10] P. M. Frank, "Advanced Fault Detection and Isolation Schemes Using Nonlinear and Robust Observers," IFAC Proc. Vol., vol. 20, no. 5, Part 3, pp. 63‑68, juill. 1987. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-6670(17)55353-7(17)55353-7
- [11] H. Hammouri, M. Kinnaert, and E. H. El Yaagoubi, "Observer-based approach to fault detection and isolation for nonlinear systems," IEEE Trans. Autom. Control, vol. 44, no. 10, pp. 1879‑1884, oct. 1999. https://doi.org/10.1109/9.793728
- [12] A. Takrouni-Hedfi, "Surveillance par observateur des systèmes dynamique hybrides," PhD Thesis, Lille 1, 2013.
- [13] Z. Kohavi, and N. K. Jha, Switching and finite automata theory. Cambridge University Press, 2009. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO978051181623
- [14] A. Balluchi, L. Benvenuti, M. D. Di Benedetto, and A. L. Sangiovanni-Vincentelli, "Design of Observers for Hybrid Systems," in Hybrid Systems: Computation and Control, Berlin, Heidelberg, 2002, pp. 76‑89. https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-45873-5_9
- [15] Z.-H. Zhang, S. Li, H. Yan, and Q.-Y. Fan, "Sliding mode switching observer-based actuator fault detection and isolation for a class of uncertain systems," Nonlinear Anal. Hybrid Syst., vol. 33, pp. 322‑335, août 2019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nahs.2019.04.001
- [16] D. Du, V. Cocquempot, and B. Jiang, "Robust fault estimation observer design for switched systems with unknown input," Appl. Math. Comput., vol. 348, pp. 70‑83, mai 2019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2018.11.034
- [17] T. Zhan, S. Ma, X. Liu, and H. Chen, "Impulsive observer design for a class of switched nonlinear systems with unknown inputs," J. Frankl. Inst., vol. 356, no. 12, pp. 6757‑6777, août 2019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfranklin.2019.05.039
- [18] M. Vidyasagar, Nonlinear Systems Analysis. Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, 2002. https://doi.org/10.1137/1.9780898719185
- [19] S. Wiggins, Introduction to applied nonlinear dynamical systems and chaos, vol. 2. Springer Science & Business Media, 2003. https://doi.org/10.1007/b97481
- [20] C. G. Cassandras and S. Lafortune, Introduction to discrete event systems. Springer Science & Business Media, 2009. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-68612-7
- [21] B. Caillaud, P. Darondeau, L. Lavagno, and X. Xie, Synthesis and control of discrete event systems. Springer Science & Business Media, 2013. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4757-6656-1
- [22] A. S. Matveev and A. V. Savkin, Qualitative theory of hybrid dynamical systems. Springer Science & Business Media, 2012. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4612-1364-2
- [23] A. J. Van Der Schaft and J. M. Schumacher, An introduction to hybrid dynamical systems, vol. 251. Springer London, 2000. https://doi.org/10.1007/BFb0109998
- [24] Q. Gaudel, "Approche intégrée de diagnostic et de pronostic pour la gestion de santé des systèmes hybrides sous incertitude," PhD Thesis, Toulouse, INSA, 2016.
- [25] S. Sastry, Nonlinear systems: analysis, stability, and control, vol. 10. Springer Science & Business Media, 2013. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4757-3108-8
- [26] J.-F. Magni and P. Mouyon, "On residual generation by observer and parity space approaches," IEEE Trans. Autom. Control, vol. 39, no. 2, pp. 441‑447, févr. 1994. https://doi.org/10.1109/9.272354
- [27] M. Staroswiecki, V. Cocquempot, and J. P. Cassar, "Observer based and parity space approaches for failure detection and identification," in IMACS-IFAC international symposium, Lille, France, 1991, vol. 25, pp. 536-541.
- [28] S. Engell, "Modelling and analysis of hybrid systems," Math. Comput. Simul., vol. 46, no. 5, pp. 445‑464, juin 1998. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-4754(98)00076-7
- [29] J. Lygeros, K. H. Johansson, S. Sastry, and M. Egerstedt, "On the existence of executions of hybrid automata," in Proceedings of 38th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control (Cat. No.99CH36304), 1999, vol. 3, pp. 2249‑2254 vol.3. https://doi.org/10.1109/CDC.1999.831255