Ch. V. Subbarao1 Department of Chemical Engineering, MVGR College of Engineering, Chintalavalasa,Vizianagaram-53005, Andhra Pradesh, India
Download Citation:
|
Download PDF
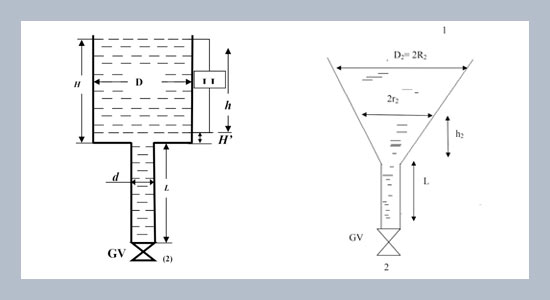
Mathematical equations for efflux time during gravity draining of a Newtonian liquid (below its bubble point) from large open storage tanks of cylindrical and conical shapes (Where the flow in the respective tanks is essentially laminar) through an exit pipe of same length and cross sectional area (the flow in the exit pipe line being turbulent) located at the bottom of the respective storage tanks are developed. The equations are ultimately simplified and written in dimensionless forms. These equations will be of use in arriving at the minimum time required for draining the contents of the respective geometries of storage vessels. To drain the same volume of liquid, the efflux time equations so developed are compared to find out which of the tanks considered drain faster.ABSTRACT
Keywords:
Efflux time; Newtonian liquid; open storage tank; exit pipe; minimum time.
Share this article with your colleagues
REFERENCES
ARTICLE INFORMATION
Accepted:
2011-04-13
Available Online:
2020-12-17
Subbarao, Ch.V. 2011. Comparison of efflux time between cylindrical and conical tanks through an exit pipe. International Journal of Applied Science and Engineering, 9, 33–41. https://doi.org/10.6703/IJASE.2011.9(1).33
Cite this article: