Vani Suthamathi Saravanarajan1, Rung-Ching Chen1*, Christine Dewi1, 2, Long-Sheng Chen1 1 Department of Information Management, Chaoyang University of Technology, Taichung, Taiwan, R.O.C.
2 Faculty of Information Technology, Satya Wacana Christian University, Central Java, Indonesia
Download Citation:
|
Download PDF
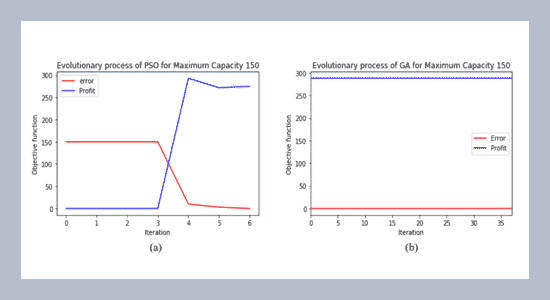
Unbound Knapsack Problems (UKP) are important research topics in many fields like portfolio and asset selection, selection of minimum raw materials to reduce the waste, and generating keys for cryptosystems. Given the uncertainty in data, capacity, and time constraints, users have to look at the possible combination of data to get maximum benefit. This paper uses UKP as a numerical model to represent different industrial combination problems. It applies Evolutionary Algorithms (EA) with Bound Constrained Strategy (BCS) to construct a search space and algorithm parameters for finding the optimal solution. Evolutionary Algorithms (EA) like Genetic Algorithms (GA) and Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) are designed based on reusable components for the algorithms to converge faster. Simulation for various objectives indicates that the GA and PSO can find the near-optimal solution in all cases. The execution time of GA and PSO for different goals and the variations in the algorithm parameters are measured. The measurement result shows the performance of GA and PSO is the same on an average for the differences in bounded constraints and parameter settings.ABSTRACT
Keywords:
Unbound knapsack problem, Constrained optimization, Genetic algorithm, Particle swarm optimization, Evolutionary algorithms.
Share this article with your colleagues
REFERENCES
ARTICLE INFORMATION
Received:
2020-08-29
Accepted:
2020-09-26
Available Online:
2021-03-01
Saravanarajan, V.S., Chen, R.-C., Dewi, C., Chen, L.-S. 2021. Solving unbounded knapsack problem using evolutionary algorithms with bound constrained strategy. International Journal of Applied Science and Engineering, 18, 2020205. https://doi.org/10.6703/IJASE.202103_18(1).002
Cite this article:
Copyright The Author(s). This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY 4.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are cited.