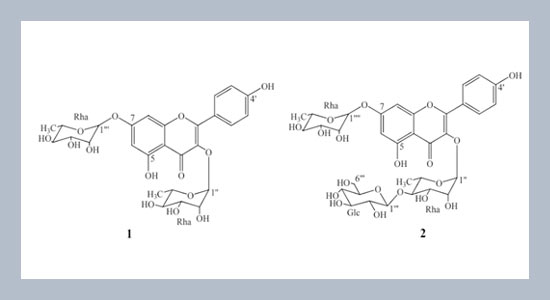
REFERENCES
- [1] Cheng, S. S., Liu, J. Y., Hsui, Y. R., Chang, S. T. 2006. Chemical polymorphism and antifungal activity of essential oils from leaves of different provenances of indigenous cinnamon (Cinnamomum osmophloeum). Bioresource Technology, 97: 306–312.
- [2] Chao, L. K., Hua, K. F., Hsu, H. Y., Cheng, S. S., Liu, J. Y., Chang, S. T. 2005. Study on the antiinflammatory activity of essential oil from leaves of Cinnamomum osmophloeum. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 53: 7274–7278.
- [3] Fang, S. H., Rao, Y. K., Tzeng, Y. M. 2004. Quantitative determination, cytotoxic and inhibitory effects of trans-cinnamaldehyde from Cinnamomum osmophloeum on human cancer cell lines but not peripheral blood mononuclear cells. International Journal of Applied Science and Engineering, 2: 136–147.
- [4] Wang, S. Y., Chen, P. F., Chang, S. T. 2005. Antifungal activities of essential oils and their constituents from indigenous cinnamon (Cinnamomum osmophloeum) leaves against wood decay fungi. Bioresource Technology, 96: 813–818.
- [5] Cheng, S. S., Liu, J. Y., Tsai, K. H., Chen, W. J., Chang, S. T. 2004. Chemical composition and mosquito larvicidal activity of essential oils from leaves of different Cinnamomum osmophloeum provenances. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 52: 4395–4400.
- [6] Fang, S. H., Rao, Y. K., Tzeng, Y. M. 2005. Inhibitory effects of flavonol glycosides from Cinnamomum osmophloeum on inflammatory mediators in LPS/IFN-γ-activated murine macrophages. Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry, 13: 2381–2388.
- [7] Woodman, O. L., Chan, E. Ch. 2004. Vascular and anti-oxidant actions of flavonols and flavones. Clinical Experimental Pharmacology and Physiology, 31: 786–790.
- [8] Rao, Y. K., Fang, S. H., Tzeng, Y. M. 2005. Synthesis, growth inhibition, and cell cycle evaluations of novel flavonoid derivatives. Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry, 13: 6850–6855.
- [9] Jorge, A. P., Horst, H., De Sousa, E., Pizzolatti, M. G., Silva, F. R. 2004. Insulinomimetic effects of kaempferitrin on glycaemia and on 14C-glucose uptake in rat soleus muscle. Chemico- Biological Interaction, 149: 89–96.
- [10] DeSousa, E., Zanatta, L., Seifriz, I., Creczynski-Pasa, T. B., Pizzolatti, M. G., Szpoganicz, B., Silva, F. R. 2004. Hypoglycemic effect and antioxidant potential of kaempferol-3,7-O-α-dirhamnoside from Bauhinia forficata leaves. Journal of Natural Products, 67: 829–832.
- [11] Yokozawa, T., Dong, E., Kawai, Y., Gemba, M., Shimizu, M. 1999. Protective effects of some flavonoids on the renal cellular membrane. Experimental Toxicology and Pathology, 51: 9–14.
- [12] Tzeng, Y. M., Chen, K., Rao, Y.K., Lee, M. J. 2009. Kaempferitrin activates the insulin signaling pathway and stimulates secretion of adiponectin in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. European Journal of Pharmacology, 607: 27–34.
- [13] Lee, M. J., Rao, Y. K., Chen, K., Lee, Y. C., Tzeng, Y.M. 2009. Effect of flavonol glycosides from Cinnamomum osmophloeum leaves on adiponectin secretion and phosphorylation of insulin receptor-β in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Journal of Ethnopharmacology (in revise).
- [14] Ying, X., Wang, R., Xu, J., Zhang, W., Li, H., Zhang, C., Li, F. 2009. HPLC determination of eight polyphenols in the leaves of Crataegus pinnatifida. Journal of Chromatogrphic Science, 47: 201–205.
- [15] Liu, J. J., Li, S. P., Wang, Y. T. 2006. Optimization for quantitative determination of four flavonoids in Epimedium by capillary zone electrophoresis coupled with diode array detection using central composite design. Journal of Chromatography A, 1103: 344–349.
- [16] Wang, S. P., Huang, K. J. 2004. Determination of flavonoids by high-performance liquid chromatography and capillary electrophoresis. Journal of Chromatography A, 1032: 273–279.
- [17] Rao, R. N., Meena, S., Rao, A. R. 2005. An overview of the recent developments in analytical methodologies for determination of COX-2 inhibitors in bulk drugs, pharmaceuticals and biological matrices. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 39: 349–363.
- [18] Mulinacci, N., Prucher, D., Peruzzi, M., Romani, A., Pinelli, P., Giaccherini, C., Vincieri, F. F. 2004. Commercial and laboratory extracts from artichoke leaves: estimation of caffeoyl esters and flavonoidic compounds content. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 34: 349–357.