Chien-Yi Chen, Cheng-Chi Tai1, Ching-Chau Su, Ju-Chu Hsieh, Jiann-Fuh Chen Department of Electrical Engineering, National Cheng Kung University
Download Citation:
|
Download PDF
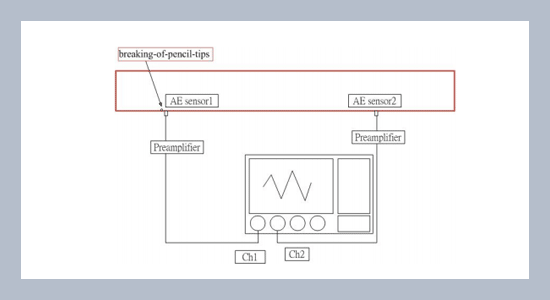
This paper focuses on the artifact breaking-of-pencil-tips experiments in metal pipes to simulate particles impacts in gas insulation switchgear (GIS). The artifact acoustic signals are generated from the breaking of pencil tips. The signals are detected and measured by means of two acoustic emission (AE) sensors. According to the analysis, the AE signals include mainly two different frequencies. The velocities of sound waves with different frequencies differ from each other as the signals are delivered in the metal pipes. Since these two kinds of sound waves are produced at the same time as the breaking of pencil tips, we can calculate the acoustic wave velocities and amplitude attenuation of waves of different frequencies according to the arrival time of the sound waves. Also, we surely can locate the particle impact position from the transmission time and distance.ABSTRACT
Keywords:
particle impact; gas insulation switchgear (GIS); source location; acoustic emission (AE).
Share this article with your colleagues
REFERENCES
ARTICLE INFORMATION
Accepted:
2009-04-10
Available Online:
2009-02-01
Chen, C.-Y., Tai, C.-C., Su, C.-C., Hsieh, J.-C., Chen, J.-F. 2009. GIS particle impact source location. International Journal of Applied Science and Engineering, 6, 223–228. https://doi.org/10.6703/IJASE.2009.6(3).223
Cite this article: