REFERENCES
- [1] C. Gupta, H. Li and M. Goto, "Deep Learning Approaches in Topics of Singing Information Processing," in IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, vol. 30, pp. 2422-2451, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1109/TASLP.2022.3190732
- [2] Hiromasa Fujihara, Masataka Goto, J.O., Okuno, H.G.: Lyric- synchronizer: Automatic synchronization system between musical audio signals and lyrics. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing 5, 1252--1261 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTSP.2011.2159577
- [3] J. Kim, H. Choi, J. Park, S. Kim, J. Kim, and M. Hahn., “Korean singing voice synthesis system based on an LSTM recurrent neural network,” in Proc. of Interspeech, pp. 1551–1555, 2018. https://doi.org/10.21437/Interspeech.2018-1575
- [4] M. Nishimura, K. Hashimoto, K. Oura, Y. Nankaku, and K. Tokuda, “Singing voice synthesis based on deep neural networks.” in Proc. of Interspeech., pp. 2478–2482, 2016. https://doi.org/10.21437/Interspeech.2016-1027
- [5] Y. Hono, K. Hashimoto, K. Oura, Y. Nankaku, and K. Tokuda., “Singing voice synthesis based on generative adversarial networks.” in Proc. of IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, pp. 6955–6959, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP.2019.8683154
- [6] Lee, J., Choi, H.S., Jeon, C.B., Koo, J., Lee, K.: “Adversarial trained end-to-end Korean singing voice synthesis system”. arXiv preprint arXiv:1908.01919 (2019). https://doi.org/10.21437/Interspeech.2019-1722
- [7] J. Li, H. Yang, W. Zhang, and L. Cai, “A lyrics to singing voice synthesis system with variable timbre,” Communications in Computer and Information Science., pp. 186– 193, 2011. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-23220-6_23
- [8] M. Freixes, F. Alıas, and J. C. Carrie, “A unit se- ´ lection text-to-speech-and-singing synthesis framework from neutral speech: proof of concept,” EURASIP Journal on
Audio, Speech, and Music Processing, vol. 2019, pp. 1–14, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13636-019-0163-y
- [9] Y. Ren, X. Tan, T. Qin, J. Luan, Z. Zhao, and T.-Y. Liu, “Deepsinger: Singing voice synthesis with data mined from the web,” in Proc. of the 26th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery Data Mining, pp. 1979–1989, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1145/3394486.3403249
- [10] Y. Jia, Y. Zhang, R. J. Weiss, Q. Wang, J. Shen, F. Ren, Z. Chen, P. Nguyen, R. Pang, I. Lopez-Moreno, and Y. Wu, “Transfer learning from speaker verification to
multispeaker text-to-speech synthesis,” Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 31 (2018), 4485-4495.
- [11] J. Parekh, P. Rao, and Y. H. Yang, “Speech-to-singing conversion in an encoder-decoder framework,” in Proc. of IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, pp. 261–265, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP40776.2020.9054473
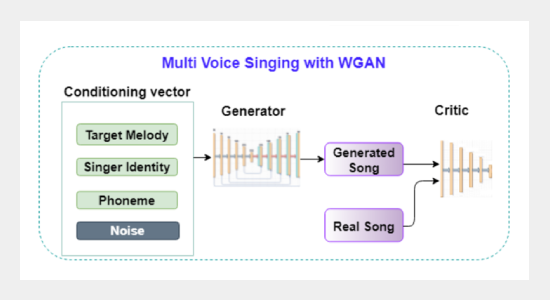
- [12] P. Chandna, M. Blaauw, J. Bonada, and E. Gomez, ´ “WGANSing: A multi-voice singing voice synthesizer based on the wasserstein-GAN,” in Proc. of 27th European Signal Processing Conference, pp. 1–5, 2019. https://doi.org/10.23919/EUSIPCO.2019.8903099
- [13] Resna, S., Rajan, R. “Multi-Voice Singing Synthesis from Lyrics”. Circuits Syst Signal Process 42, 307–321 2023. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-022-02122-3
- [14] L. Su, “Vocal melody extraction using patch-based CNN,” in Proc. of IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, pp. 371–375, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP.2018.8462420
- [15] B. McFee, C. Raffel, D. Liang, D. Ellis, M. Mcvicar, E. Battenberg, and O. Nieto, “Librosa: Audio and music signal analysis in python,” in Proc. of 14th Python in Science Conference, pp. 18–24, 01 2015. https://doi.org/10.25080/Majora-7b98e3ed-003
- [16] Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., Brox, T.: U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: N. Navab, J. Hornegger, W.M. Wells, A.F. Frangi (eds.) Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2015, pp. 234–241. Springer International Publishing, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-
24574-4_28
- [17] D. Griffin and Jae Lim, "Signal estimation from modified short-time Fourier transform," in IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, vol. 32, no. 2, pp. 236-243, April 1984. https://doi.org/10.1109/TASSP.1984.1164317
- [18] Radford, A., Metz, L., Chintala, S.: “Unsupervised representation learning with deep convolutional generative adversarial networks.”, in Proc. of 4th International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR, 2016.
- [19] van den Oord, A., Dieleman, S., Zen, H., Simonyan, K., Vinyals, O., Graves, A., Kalchbrenner, N., Senior, A., Kavukcuoglu, K.: Wavenet: A generative model for raw audio. In: Arxiv (2016).
- [20] Blaauw, Merlijn, and Jordi Bonada. "A Neural Parametric Singing Synthesizer Modeling Timbre and Expression from Natural Songs" Applied Sciences 7, no. 12: 1313, 2017. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7121313
- [21] Morise, M., Yokomori, F., Ozawa, K.: World: A vocoder-based high-quality speech synthesis system for real-time applications. IEICE Transactions on Information and Systems E99.D, 1877–1884 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1587/transinf.2015EDP7457
- [22] A. Pandey and D. Wang, "On Cross-Corpus Generalization of Deep Learning Based Speech Enhancement," in IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, vol. 28, pp. 2489-2499, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1109/TASLP.2020.3016487
- [23] A. Nagrani, J. S. Chung, W. Xie, and A. Zisserman, “Voxceleb: Large-scale speaker verification in the wild,” Computer Speech Language, vol. 60, pp. 1010–27, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csl.2019.101027
- [24] Z. Duan, H. Fang, B. Li, K. C. Sim, and Y. Wang, “The nus sung and spoken lyrics corpus: A quantitative comparison of singing and speech,” in Proc. of Asia-Pacific Signal and Information Processing Association Annual Summit and Conference, pp. 1–9, 2013. https://doi.org/10.1109/APSIPA.2013.6694316