REFERENCES
- [1] Indian Pharmacopoeia, Vol 2, Government of India Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, published by The Indian Pharmacopoeia Commission, Ghaziabad, 2007, pp 1071-1072.
- [2] International Pharmacopoeia Monograph on Efavirenz, World Health Organization, published by the World Health. Organization, Geneva, Switzerland, 2005.
- [3] Adkins, J. C. and Noble, S. 1998. Efavirenz. Drugs, 56: 1055-1064.
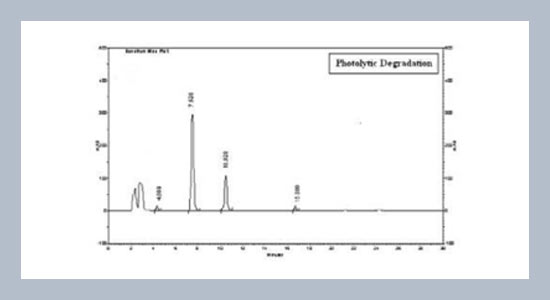
- [4] Phale, M. D. and Hamrapurkar, P. D. 2010. Optimization and Establishment of a Validated Stability-Indicating HPLC Method for Study of the Stress Degradation Behavior of Metoprolol Succinate. Journal of AOAC International, 93: 911-916.
- [5] Woolf E. J., Matthews, C. Z., Mazenko R. S., Wiener, H., Eng, C. M., Constanzer, M.L., Doss, G. A., and Matuszewski, B.K. 2002. Determination of Efavirenz, a selective non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor, in human plasma using HPLC with post-column photochemical derivatization and fluorescence detection. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 28: 925-934.
- [6] Raras-Nacenta, M. S., Lopz-Pua, Y. L., Cortes, L. F. L., Mallolas, J., Gatell, J. M., and Carne, X. 2001. Determination of Efavirenz in human Plasma by high-performance Liquid Chromato- graphy with ultraviolet detection. Journal of Chromatography B Biomedical Applications, 763: 53-59.
- [7] Villani, P., Massimo, P. M., Banfo, S., Rettani, M., Burroni, D., and Seminari, E. 1999. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Method for Analyzing the Antiretroviral Agent Efavirenz in Human Plasma. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring, 21: 346-350.
- [8] Langmann, P., Schirmer, D., Vath, T., Zilly, M., and Klinker, H. 2001. High-performance liquid chromatographic method for the determination of HIV-1 non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor Efavirenz in plasma of patients during highly active antiretroviral therapy. Journal of Chromatography B Biomedical Applications, 755: 151-156.
- [9] Veldkamp, A. I., Heeswijk, R. P., Meenhorst, P. L., Mulder, J. W., Lange. J. M., Beijnen, J. H., and Hoetelmans, R. M. 1999. Quantitative determination of Efavirenz (DMP 266), a novel non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor, in human plasma using isocratic reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography with ultraviolet detection. Journal of Chromatography B Biomedical Applications, 734: 55-61.
- [10] Ribeiro, J. A., Campos, L. M., Alves, R. J., Lages, G. P., and Pianetti, G. A. 2007. Efavirenz related compounds preparation by hydrolysis procedure: setting reference standards for chromatographic purity analysis. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 43: 298-303.
- [11] Weissburg, R. P., Montgomery, E. R., Junnier, L. A., Segretario, J., Cook, S., and Hovsepian, P. K. 2002. Investigation of critical factors for the resolution of SR695, a key impurity, from Efavirenz in reversed-phase assay of Efavirenz dosage forms. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 28: 45-56.
- [12] Montgomery, E. R., Edmanson, A. L., Cook, S. C., and Hovsepian, P. K. 2001. Development and validation of a reversed-phase HPLC method for analysis of Efavirenz and its related substances in the drug substance and in a capsule formulation. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 25: 267-284.
- [13] Hamrapurkar, P., Phale, M., and Shah, N. 2009. Quantitative estimation of Efavirenz by high performance thin layer chromatography. Journal of Young Pharmacists, 1: 359-363.
- [14] Aymard, G., Legrand, M., Trichereau, N., and Diquet, B. 2000. Determination of twelve antiretroviral agents in human plasma sample using reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. Journal of Chromatography B Biomedical Applications, 744: 227-240.
- [15] Fan, B., and Stewart, J. T. 2002. Determination of Stavudine/ Didanosine/ Saquinavir and Stavudine/Didanosine/ Efavirenz in Human Serum By Micellar Electrokinetic Chromatography (Mekc). Journal of Liquid Chromatography & Related Technologies, 25: 937-947.
- [16] Lemmer, P., Schneider, S., Schuman, M., Omes, C., Arendt, V., and Tayari, J. C. 2005. Determination of nevirapine and Efavirenz in plasma using GC/MS in selected ion monitoring mode. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring, 27: 521-525.
- [17] Wolfgang, E. J., Matthias, U., Claus, N., Muhammad, B., Sumiko, H., Leslie, Z. B., and Uwe, C. 2004. Automated, fast, and sensitive quantification of drugs in human plasma by LC/LC-MS: quantification of 6 protease inhibitors and 3 nonnucleoside transcriptase inhibitors. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring, 26: 546-562.
- [18] Pereira, E. A., Micke, G. A., and Tavares, M. F. 2005. Determination of antiretroviral agents in human serum by capillary electrophoresis. Journal of Chromatography A, 1091:169-176.
- [19] Takahashi, M., Yoshida, M., Oki, T., Okumura, N., Suzuki, T., and Kaneda, T. 2005. Conventional HPLC method used for simultaneous determination of the seven HIV protease inhibitors and nonnucleoside reverse transcription inhibitor Efavirenz in human plasma. Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 28: 1286-1290.
- [20] Rouzes, A., Berthoin, K., Xuereb, F., Djabarouti, S., Pellegrin, I., and Pellegrin, J. L. 2004. Simultaneous determination of the antiretroviral agents: amprenavir, lopinavir, ritonavir, saquinavir and Efavirenz in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells by high-performance liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry. Journal of Chromatography B Biomedical Applications, 813: 209–216.
- [21] Bin, F., Bartlett, M. G., and Stewart, J. T. 2002. Determination of lamivudine/stavudine/ Efavirenz in human serum using liquid chromatography/electrospray tandem mass spectrometry with ionization polarity switch. Biomedical Chromatography, 16: 383-389.
- [22] Colombo, S., Beguin, A., Telenti, A., Biollaz, J., Buclin, T., and Rochat, B. 2005. Intracellular measurements of anti-HIV drugs indinavir, amprenavir, saquinavir, ritonavir, nelfinavir, lopinavir, atazanavir, Efavirenz and nevirapine in peripheral blood mononuclear cells by liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry. Journal of Chromatography B Biomedical Applications, 819: 259-276.
- [23] Rentsch, K. M. 2003. Sensitive and specific determination of eight antiretroviral agents in plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Journal of Chromatography B Biomedical Applications, 788: 339-350.
- [24] Volosov, A., Alexander, C., Ting, L., and Soldin, S. 2002. Simple rapid method for quantification of antiretrovirals by liquid chromatography-tandem mass-spectrometry. Clinical Biochemistry, 35: 99-103.
- [25] Kappelhoff, B. S., Rosing, H., Huitema, A. D. R., and Beijnen, J. H. 2003. Simple and rapid method for the simultaneous determination of the non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors Efavirenz and nevirapine in human plasma using liquid chromatography. Journal of Chromatography B Biomedical Applications, 792: 353–362.
- [26] Moal, G. L., Venisse, N., and Faux, J. 2003. Simultaneous Determination of Six HIV Protease Inhibitors, One Metabolite, and Two Non-nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors in Human Plasma by Isocratic Reversed-Phase Liquid Chromatography After Solid-Phase Extraction. Chromatographia, 58: 421-426.
- [27] Hirabayashi, Y., Tsuchiya, K., Kimura, S., and Oka, S. 2006. Simultaneous determination of six HIV protease inhibitors (amprenavir, indinavir, lopinavir, nelfinavir, ritonavir and saquinavir), the active metabolite of nelfinavir (M8) and non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (Efavirenz) in human plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography. Biomedical Chromatography, 20: 28-36.
- [28] Dailly, E., Raffi, F., and Jolliet, P. J. 2004. Determination of atazanavir and other antiretroviral drugs (indinavir, amprenavir, nelfinavir and its active metabolite M8, saquinavir, ritonavir, lopinavir, nevirapine and Efavirenz) plasma levels by high performance liquid chromatography with UV detection. Journal of Chromatography B Biomedical Applications, 813: 353-358.
- [29] Poirier, J. M., Robidou, P., and Jaillon, P. 2005. Simple and Simultaneous Determination of the HIV-Protease Inhibitors Amprenavir, Atazanavir, Indinavir, Lopinavir, Nelfinavir, Ritonavir and Saquinavir Plus M8 Nelfinavir Metabolite and the Nonnucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors Efavirenz and Nevirapine in Human Plasma by Reversed-Phase Liquid Chromatography. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring, 27: 186-192.
- [30] Poirier, J.M., Robidou, P., and Jaillon, P. 2002. Simultaneous determination of the six HIV protease inhibitors (amprenavir, indinavir, lopinavir, nelfinavir, ritonavir, and saquinavir) plus M8 nelfinavir metabolite and the nonnucleoside reverse transcription inhibitor Efavirenz in human plasma by solid-phase extraction and column liquid chromatography. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring, 24: 302-309.
- [31] Keil, K., Frerichs, V. A., DiFrancesco, R., and Morse, G. 2003. Reverse phase high-performance liquid chromatography method for the analysis of amprenavir, Efavirenz, indinavir, lopinavir, nelfinavir and its active metabolite (m8), ritonavir, and saquinavir in heparinized human plasma. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring, 25: 340–346.
- [32] Boffito, M., Tija, J., Reynolds, H. E., Hoggard, P. G., Bonora, S., Di Perri, G., and Back, D. J. 2002. Simultaneous determination of rifampicin and Efavirenz in plasma. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring, 24: 670-674.
- [33] Turner, M. L., Walker, K. R., King, J. R., and Acosta, E. P. 2003. Simultaneous determination of nine antiretroviral compounds in human plasma using liquid chromatography. Journal of Chromatography B Biomedical Applications, 784: 331-341.
- [34] Rezk, N. L., Tidwell, R. R., and Kashuba, A. D. 2002. Simple and rapid quantification of the nonnucleoside reverse transciptase inhibitors nevirapine, delavirdine, and Efavirenz in human blood plasma using high-performance liquid chromatography with ultraviolet detection. Journal of Chromatography B, 774: 79–88.
- [35] Rezk, N. L., Tidwell, R. R., and Kashuba, A. D. 2004. High-performance liquid chromatography assay for the quantification of HIV protease inhibitors and non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors in human plasma. Journal of Chromatography B, 805: 241–347.
- [36] Notari, S., Bocedi, A., Ippolito, G., Narciso, P., Pucillo, L. P., Tossini, G., Donnorso, R. P., Gasparrini, F., and Ascenzi, P. 2006. Simultaneous determination of 16 anti-HIV drugs in human plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography. Journal of Chromatography B Biomedical Applications, 831: 258-266.
- [37] Proust, V., Toth, K., Hulin, A., Taburet, A. M., Gimenez, F., and Singlas, E. 2000. Simultaneous high-performance liquid chromatographic determination of the antiretroviral agents amprenavir, nelfinavir, ritonavir, saquinavir, delavirdine and Efavirenz in human plasma. Journal of Chromatography B Biomedical Applications, 742: 453-458.
- [38] ICH [Stability Testing of New Drug Substances and Products (Q1AR2)], International Conference on Harmonization, Food and Drug Administration, Geneva, Switzerland, 2003.