Rajaneesh N. Marigoudara,* and Kanakuppi Sadashivappab aDepartment of Mechanical Engineering, GM Institute of Technology, Davangere, Karnataka, India
bDepartment of IPE, Bapuji Institute of Engineering and Technology, Davangere, Karnataka, India
Download Citation:
|
Download PDF
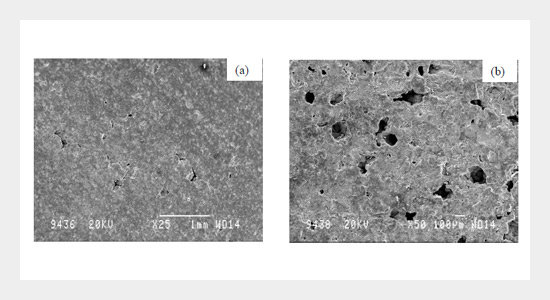
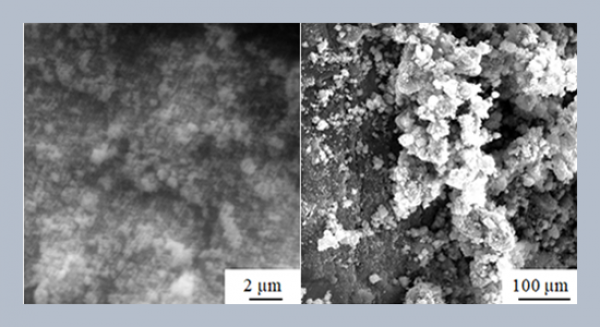
The present work emphasis on behavior of zinc-aluminium alloy reinforced with silicon carbide particles when machined with wire electric discharge machining process (WEDM). The difficulty faced by conventional machining is severe tool damage while machining metal matrix composites. Electrical discharge machining can be successfully employed for machining MMC in the place of conventional machining to reduce the tool damage and to produce complicated contours with superior finish. In the present study ZA43 reinforced with SiCp is machined by wire EDM process. Machining is carried-out by varying applied current of (2, 4 and 6amp.), pulse on time (4, 8 and 16µs) and pulse off time (5, 7 and 9µs) while other parameters such as voltage, dielectric flushing pressure, wire tension etc. are maintained constant. It is observed that reduction in the material removal rate and increase in surface roughness for increasing reinforcement percentage in the composite. It is also observed that applied current and pulse on time increases the material removal rate where as pulse off time has less effect on it.ABSTRACT
Keywords:
WEDM; MMC; pulse-on time; pulse-off time; dielectric liquid; surface roughness; material removal rate.
Share this article with your colleagues
[1] Patil, N. G. and Brahmankar, P. K. 2010. Determination of material removal rate in wire electro-discharge machining of metal matrix composites using dimensional analysis. International Journal of Advance Manufacturing Technology, 51: 599-610.REFERENCES
[2] Patil, N. G. and Brahmankar, P. K. 2010. Some studies into wire electro-discharge machining of alumina particulate-reinforced aluminum matrix composites. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 48: 537-555.
[3] Mouangue Nanimina, A., Abdul-Rani, A. M., Ahmad, F., Zainuddin, A., and Jason Lo, S. H. 2011. Effects of Electro-discharge machining on Aluminium Metal matrix composites. Journal of Applied Sciences, 11: 1668-1672.
[4] Pandey, A. and Singh, S. 2010. Current research trends in variants of Electrical Discharge Machining: A review. International journal of Engineering science and Technology, 2: 2172-2191.
[5] Kathiresan M. and Sornakumar T. 2010. EDM Studies on Aluminum Alloy-Silicon Carbide Composites Developed by Vortex Technique and Pressure Die Casting. Journal of Minerals and Materials characterization & Engineering, 9: 79-88.
[6] Singh, H. and Garg, R. 2009. Effects of process parameters on material removal rate in WEDM. Journal of Achievements in Materials and Manufacturing Engineering, 32: 70-74.
[7] Garg, R. K., Singh, K. K., Sachdeva, A., Sharma, V. S., Ojha, K., and Singh, S. 2010. Review of research work in sinking EDM and WEDM on metal matrix composite materials. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 50: 611-624.
[8] Narender Singh, P., Raghukandan, K., Rathinasabapathi, M., and Pai, B. C. 2004. Electric discharge machining of Al-10% SiCP as-cast metal matrix composites. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 155-156, 30: 1653-1657.
[9] Mahapatra, S. S. and Amar, P. 2006. Optimization of wire electrical discharge machining (WEDM) process parameters using Taguchi method. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 34: 911-925.
[10] Pasam, V. K., Battula, S. B., Madar, V. P., and Swapna, M. 2010. Optimizing Surface Finish in WEDM Using the Taguchi Parameter Design Method. Journal of the Brazilian Society of Mechanical Science & Engineering, 32: 107-113.
[11] Rao, P. S., Ramji, K., and Satyanarayana, B. 2010. Prediction of Material removal rate for Aluminum BIS-24345 Alloy in wire-cut EDM. International Journal of Engineering Science and Technology, 2: 7729-7739.
[12] Ahmad, R. N., Derman, M. N., and Marzuki, M. 2010. Primary study on machinability of aluminium matrix composite using WEDM. International Journal of Engineering & Technology, 10: 145-150.
[13] Sanchez, H. T., Estrems, M., and Faura, F. 2011. Development of an inversion model for establishing EDM input parameters to satisfy material removal rate, electrode wear ratio and surface roughness. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 57: 189-201.
[14] Ramulu, M. and Taya, M. 1989. EDM machinability of SiCw/Al composites. Journal of Material Science, 24: 1103-1108.
[15] Tosun, N. 2003. The Effect of the Cutting Parameters on Performance of WEDM. KSME International Journal, 17: 816-824.
[16] Satishkumar, D., Kanthababu, M., Vajjiravelu, V., Anburaj, R., Thirumalai Sundarrajan, and Arul, H. 2011. Investigation of wire electrical discharge machining characteristics of Al6063/SiCp composites. International Journal of Advance Manufacturing Technology, 56: 975-986.
[17] Xie, X.., Zhang, D., and Liu, J. 2001. Thermal expansion properties of TiC particle reinforced ZA 43 matrix composites. Materials and Design, 22: 157-162.
[18] Veeresh Kumar, G. B., Rao, C. S. P., Selvaraj, N., and Bhagyashekar, M. S. 2010. Studies on Al6061-SiC and Al7075-Al2O3 Metal Matrix Composites. Journal of Minerals and Material Characterization & Engineering, 9: 43-55.
ARTICLE INFORMATION
Received:
2012-05-18
Revised:
2012-12-05
Accepted:
2013-04-16
Available Online:
2013-09-01
Marigoudar, R.N., Sadashivappa, K. 2013. Effect of machining parameters on MRR and surface roughness in machining of ZA43/ SiCp composite by WEDM. International Journal of Applied Science and Engineering, 11, 317–330. https://doi.org/10.6703/IJASE.2013.11(3).317
Cite this article: