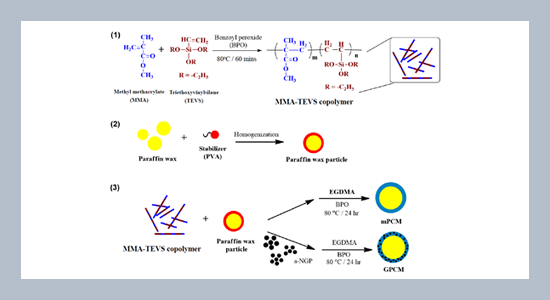
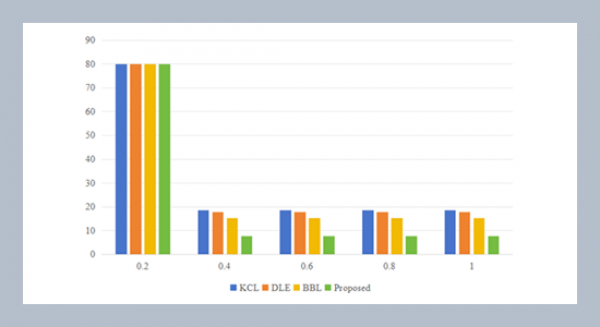
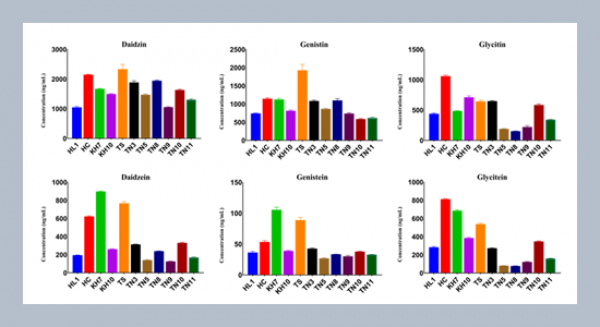
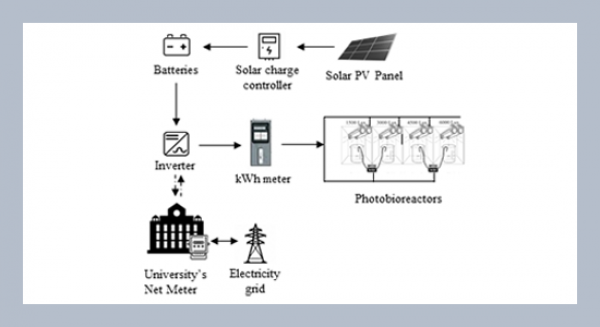
REFERENCES
- Bao, M., Lou, X., Zhou, Q., Dong, W., Yuan, H., Zhang, Y. 2014. Electrospun biomimetic fibrous scaffold from shape memory polymer of pdlla-co-tmc for bone tissue engineering. ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces, 6(4), 2611–2621.
- Chen, Z., Wang, J., Yu, F., Zhang, Z., Gao, X. 2015. Preparation and properties of graphene oxide-modified poly(melamine-formaldehyde) microcapsules containing phase change material n-dodecanol for thermal energy storage. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 3(21), 11624–11630.
- El Feninat, F., Laroche, G., Fiset, M., Mantovani, D. 2002. Shape memory materials for biomedical applications. Advanced Engineering Materials, 4(3), 91–104.
- Hassan, A., Shakeel Laghari, M., Rashid, Y. 2016. Micro-encapsulated phase change materials: A review of encapsulation, safety and thermal characteristics. Sustainability, 8(10), 1046.
- Hassan H., Hallez H., Thielemans W., Vandeginste V. 2024. A review of electro-active shape memory polymer composites: Materials engineering strategies for shape memory enhancement. European Polymer Journal, 208, 112861.
- He, X., Zhang, L., Li, C. 2021. PEG-based polyurethane/ Paraffin@SiO2/ Boron nitride phase change composite with efficient thermal conductive pathways and superior mechanical property. Composites Communications, 25, 100609.
- Herath M., Epaarachchi J., Islam M., Fang L., Leng J. 2020. Light activated shape memory polymers and composites: A review. European Polymer Journal, 136, 109912.
- Jamekhorshid, A., Sadrameli, S.M. Farid, M. 2014. A review of microencapsulation methods of phase change materials (PCMs) as a thermal energy storage (TES) medium. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 31, 531–542.
- Jing, J.-H., Wu, H.-Y., Shao, Y.-W., Qi, X.-D., Yang, J.-H., Wang, Y. 2019. Melamine foam-supported form-stable phase change materials with simultaneous thermal energy storage and shape memory properties for thermal management of electronic devices. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 11(21), 19252–19259.
- Kaliyannan, G.V., Rajasekar, R., Gunasekaran, R., Anbupalani, M.S., Chinnasamy, M., Palaniappan, S.K. 2022. Doping of carbon nanostructures for energy application. In: Sahoo, S., Tiwari, S.K., Das, A.K. (eds) Defect Engineering of Carbon Nanostructures. Advances in Material Research and Technology. Springer, Cham, 83–109.
- Kim, B.K., Lee, S.Y., Xu, M. 1996. Polyurethanes having shape memory effects. Polymer, 37(26), 5781–5793.
- Koca, H.D., Turgut, A., Evgin, T., Ateş, I., Chirtoc, M., Šlouf, M., Omastová, M. 2023. A comprehensive study on the thermal and electrical conductivity of EPDM composites with hybrid carbon fillers. Diamond and Related Materials, 139, 110289.
- Koerner, H., Price, G., Pearce, N.A., Alexander, M., Vaia, R.A. 2004. Remotely actuated polymer nanocomposites—stress-recovery of carbon-nanotube-filled thermoplastic elastomers. Nature Materials, 3(2), 115–120.
- Kumar, P.S., Rajasekar, R., Sivasenapathy, C., Pal, S.K. 2020. Development of shape memory alloy based quarter car suspension system. Journal of Mechanical Engineering Research, 3(1), 21–24.
- Langer, R., Tirrell, D.A. 2004. Designing materials for biology and medicine. Nature, 428(6982), 487–492.
- Lendlein, A., Gould, O.E.C. 2019. Reprogrammable recovery and actuation behaviour of shape-memory polymers. Nature Reviews Materials, 4(2), 116–133.
- Li, W., Xu, L., Wang, X., Zhu, R., Yan, Y. 2022. Phase change energy storage elastic fiber: A simple route to personal thermal management. Polymers, 14(1), 53.
- Liu, Q., Li, M., Gu, Y., Wang, S., Zhang, Y., Li, Q., Gao, L., Zhang, Z. 2015. Interlocked CNT networks with high damping and storage modulus. Carbon, 86, 46–53.
- Liu, Y., Du, H., Liu, L., Leng, J. 2014. Shape memory polymers and their composites in aerospace applications: A review. Smart Materials and Structures, 23(2), 023001.
- Mather, P.T., Luo, X., Rousseau, I.A. 2009. Shape memory polymer research. Annual Review of Materials Research, 39(1), 445–471.
- Mineart, K.P., Tallury, S.S., Li, T., Lee, B., Spontak, R.J. 2016. Phase-change thermoplastic elastomer blends for tunable shape memory by physical design. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 55(49), 12590–12597.
- Parvate, S., Singh, J., Dixit, P., Vennapusa, J.R., Maiti, T.K., Chattopadhyay, S. 2021. Titanium dioxide nanoparticle-decorated polymer microcapsules enclosing phase change material for thermal energy storage and photocatalysis. ACS Applied Polymer Materials, 3(4), 1866–1879.
- Peng, G., Dou, G., Hu, Y., Sun, Y., Chen, Z. 2020. Phase change material (PCM) microcapsules for thermal energy storage. Advances in Polymer Technology, 2020, 9490873.
- Pilate, F., Toncheva, A., Dubois, P., Raquez, J.-M. 2016. Shape-memory polymers for multiple applications in the materials world. European Polymer Journal, 80, 268–294.
- Rajasekar, R., Sahoo, S., Lee, J.H., Das, A.K., Somasundaram M., Palaniappan S.K., Sivaraj S. 2021. Carbon-based multi-layered films for electronic application: A Review. Journal of Electronic Materials, 50(4), 1845–1892.
- Shih, Y.-F., Chen, P.T., Lau, E.M., Hsu, L.R. 2021. Thermally conductive microcapsule/high-density polyethylene composite for energy saving and storage. Modern Physics Letters B, 35(24), 2150429.
- Su, J.-F., Wang, X.-Y., Han, S., Zhang, X.-L., Guo, Y.-D., Wang, Y.-Y., Tan, Y.-Q., Han, N.-X., Li, W. 2017. Preparation and physicochemical properties of microcapsules containing phase-change material with graphene/organic hybrid structure shells. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 5(45), 23937–23951.
- Sun, L., Huang, W.M., Ding, Z., Zhao, Y., Wang, C.C., Purnawali, H., Tang, C. 2012. Stimulus-responsive shape memory materials: A review. Materials & Design, 33, 577–640.
- Sun, W., Wang, X., Zhang, X., Kong, X. 2020. Design and synthesis of microencapsulated phase-change materials with a poly(divinylbenzene)/dioxide titanium hybrid shell for energy storage and formaldehyde photodegradation. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 124(38), 20806–20815.
- Wan, X., He, Y., Liu, Y., Leng, J. 2022. 4D printing of multiple shape memory polymer and nanocomposites with biocompatible, programmable and selectively actuated properties. Additive Manufacturing, 53, 102689.
- Wang, H., Zhao, L., Chen, L., Song, G., Tang, G. 2017. Facile and low energy consumption synthesis of microencapsulated phase change materials with hybrid shell for thermal energy storage. Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 111, 207–213.
- Wang, J., Xue, Z., Li, G., Wang, Y., Fu, X., Zhong, W.-H., Yang, X. 2018. A UV-curable epoxy with “soft” segments for 3D-printable shape-memory materials. Journal of Materials Science, 53(17), 12650–12661.
- Wang, M., Sayed, S. M., Guo, L.-X., Lin, B.-P., Zhang, X.-Q., Sun, Y., Yang, H. 2016. Multi-stimuli responsive carbon nanotube incorporated polysiloxane azobenzene liquid crystalline elastomer composites. Macromolecules, 49(2), 663–671.
- Wu, C.-H., Chen, Y.-C., Dai, S.A., Chen, S.-C., Tung, S.-H., Lee, R.-H., Su, W.-C., Jeng, R.-J. 2017. Iterative synthesis of monodisperse pendants for making comb-like polyurethanes. Polymer, 119, 1–12.
- Wu, C.-H., Huang, Y.-C., Chen, W.-L., Lin, Y.-Y., Dai, S.A., Tung, S.-H., Jeng, R.-J. 2020a. Size-dependent phase separation and thermomechanical properties of thermoplastic polyurethanes. Polymer, 210, 123075.
- Wu, C.-H., Shau, S.-M., Liu, S.-C., Dai, SA., Chen, S.-C., Lee, R.-H., Hsieh, C.-F., Jeng, R.-J. 2015. Enhanced shape memory performance of polyurethanes via the incorporation of organic or inorganic networks. RSC Advances, 5(22), 16897–16910.
- Wu, H.-Y., Chen, R.-T, Shao, Y.-W., QI, X.-D., Yang, J.-H.,Wang, Y. 2019a. Novel flexible phase change materials with mussel-inspired modification of melamine foam for simultaneous light-actuated shape memory and light-to-thermal energy storage capability. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 7(15), 13532–13542.
- Wu, H.-Y., Li, S.-T., Shao, Y.-W., Jin, X.-Z., QI, X.-D., Yang, J.-H., Zhou, Z.-W., Wang, Y. 2020b. Melamine foam/reduced graphene oxide supported form-stable phase change materials with simultaneous shape memory property and light-to-thermal energy storage capability. Chemical Engineering Journal, 379, 122373.
- Wu, H., Deng, S., Shao, Y., Yang, J., Qi, X., Wang, Y. 2019b. Multiresponsive shape-adaptable phase change materials with cellulose nanofiber/graphene nanoplatelet hybrid-coated melamine foam for light/electro-to-thermal energy storage and utilization. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 11(50), 46851–46863.
- Wu, T., Hu, Y., Rong, H., Wang, C. 2021. SEBS-based composite phase change material with thermal shape memory for thermal management applications. Energy, 221, 119900.
- Xia, Y., He, Y., Zhang, F., Liu, Y., Leng, J. 2021. A review of shape memory polymers and composites: Mechanisms, materials, and applications. Advanced Materials, 33(6), 2000713.
- Xiao, X., Kong, D., Qiu, X., Zhang, W., Liu, Y., Zhang, S., Zhang, F., Hu, Y., Leng, J. 2015. Shape memory polymers with high and low temperature resistant properties. Scientific Reports, 5(1), 14137.
- Yu, K., Liu, Y., Leng, J. 2014. Shape memory polymer/CNT composites and their microwave induced shape memory behaviors. RSC Advances, 4(6), 2961–2968.
- Zarek, M., Layani, M., Cooperstein, I., Sachyani, E., Cohn, D., Magdassi, S. 2016. 3D Printing: 3D printing of shape memory polymers for flexible electronic devices. Advanced Materials, 28(22), 4166–4166.
- Zhang, D., Liu, L., Lan, X., Leng, J., Liu, Y. 2022. Synchronous deployed design concept triggered by carbon fibre reinforced shape memory polymer composites. Composite Structures, 290, 115513.
- Zhang, L., Yang, W., Jiang, Z., He, F., Zhang, K., Fan, J., Wu, J. 2017. Graphene oxide-modified microencapsulated phase change materials with high encapsulation capacity and enhanced leakage-prevention performance. Applied Energy, 197, 354–363.
- Zhang, Q., Cui, K., Feng, J., Fan, J., Li, L., Wu, L., Huang, Q. 2015. Investigation on the recovery performance of olefin block copolymer/hexadecane form stable phase change materials with shape memory properties. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 132, 632–639.
- Zhang, Q., Feng, J. 2013. Difunctional olefin block copolymer/paraffin form-stable phase change materials with simultaneous shape memory property. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 117, 259–266.
- Zhao, Q., QI, H. J., Xie, T. 2015. Recent progress in shape memory polymer: New behavior, enabling materials, and mechanistic understanding. Progress in Polymer Science, 49-50, 79–120.
- Zhao, W., Liu, L., Zhang, F., Leng, J., Liu, Y. 2019. Shape memory polymers and their composites in biomedical applications. Materials Science and Engineering: C, 97, 864–883.