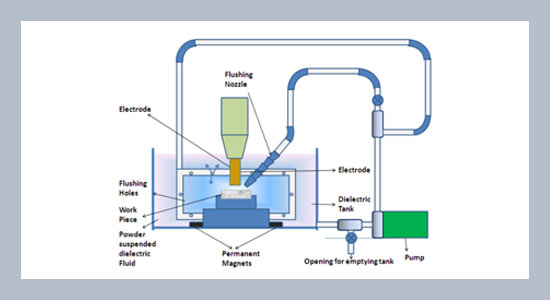
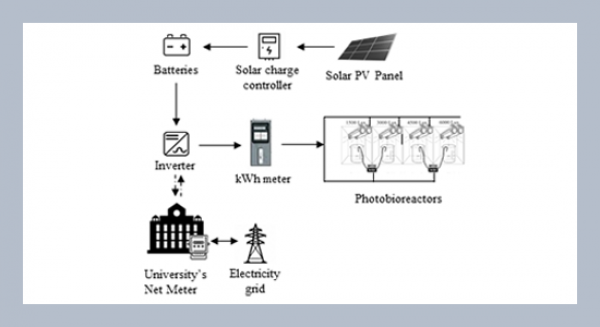
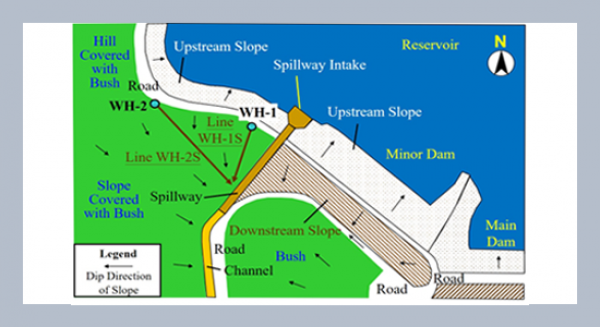
REFERENCES
- [1] Cogun, C., Ozerkan, B., Karacay, T. 2006. An experimental investigation on the effect of powder mixed dielectric on machining performance in electrical discharge machining. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part B: Journal of Engineering Manufacture 220 Part B, 220: 1035-1050.
- [2] Erden, A. and Bilgin, S. 1980. Role of impurities in electric discharge machining. in: Proceedings of the 21st International Machine Tool Design and Research Conference, Macmillan, London, 345-350.
- [3] Furutani, K., Saneto, A., Takezawa, H., Mohri, N., and Miyake, H. 2001. Accertation of titanium carbide by electrical discharge machining with powder suspended in working fluid. Precision Engineering, 25: 138-144.
- [4] Furutani, K. and Shiraki, K. 2002. Deposition of lubricant layer during finishing process by electrical discharge machining with molybdenum disulphide powder suspended in working fluid. in: JSME/ ASME International Conference on Materials and Processing, 468-473.
- [5] Garg, R. K., Singh, K. K., Sachdeva, A., Sharma, V., and Ojha, K. 2010. Review of research work in sinking EDM and WEDM on metal matrix composite materials. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 50, 5-8, 611-624.
- [6] Prihandana, G. S., Mahardika, M., Hamdi, M., Wong, Y. S., and Mitsui, K. 2009. Effect of micro-powder suspension and ultrasonic vibration of dielectric fluid in micro-EDM processes-Taguchi approach. International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, 49, 1035-1041.
- [7] Guven, G., Perendeci, A., Tanyolac, A., and Hazard, J. 2008. Mater. 151, 69-78.
- [8] Chow, H. M., Yan, B. H., Huang, F. Y. and Hung, J., C. 2000. Study of added powder in kerosene for the micro-slit machining of titanium alloy using electro-discharge machining. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 101: 95- 103.
- [9] Jeswani, M. L. 1981. Effects of the addition of graphite powder to kerosene used as the dielectric fluid in electrical discharge machining. Wear, 70: 133-139.
- [10] Kansal, H. K., Singh, S., and Kumar, P., 2003. State of the art concerning powder mixed EDM. in: Proceedings of the International Conference on Emerging Technology (ICET-2003) KIIT, Bhubansewar, India.
- [11] Kansal, H. K., Singh, S., and Kumar, P. 2005. Parametric optimization of powder mixed electrical discharge machining by response surface methodology. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 169, 427-436.
- [12] Kansal, H. K., Singh, S., and Kumar, P. 2007. Effect of Silicon powder mixed EDM on machining rate of AISI D2 die Steel. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 9, 1: 13-22.
- [13] Ojha, K., Garg, R. K., and Singh, K. K. 2011. The Effect of Nickel Micro Powder Suspended Dielectric on EDM Performance Measures of EN-19 Steel. Journal of Engineering and Applied Sciences, 6, 1: 27-37.
- [14] Ojha, K., Garg, R. K., and Singh, K. K. 2011. An overview of technology and research in electrode design and manufacturing in sinking electrical discharge machining. Journal of Engineering science and Technology review (Accepted for publication-In press)
- [15] Ojha, K., Garg, R. K., and Singh, K. K., 2010. MRR Improvement in Sinking Electrical Discharge Machining: A Review. Journal of Minerals and Materials Characterization and Engineering, 9, 8: 709-739.
- [16] Furutani, K., Sato, H., and Suzuki, M. 2009. Influence of electrical conditions on performance of electrical discharge machining with powder suspended in working oil for titanium carbide deposition process. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 40: 1093-1101.
- [17] Kobayashi, K., Magara, T., Ozaki, Y., and Yatomi, T., 1992. The present and future developments of electrical discharge machining, in: Proceedings of 2nd International Conference on Die and Mould Technology, Singapore, 35-47.
- [18] Kung, K. Y., Horng, J. T., and Chiang, K. T., 2009. Material removal rate and electrode wear ratio study on the powder mixed electrical discharge machining of cobalt-bonded tungsten carbide, Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 40: 95-104.
- [19] Kunieda, M. and Yanatori, K. 1997. Study on debris movement in EDM gap. International Journal of Electrical Machining, 2, 43-49.
- [20] Luo, Y. F. 1997. The dependence of interspace discharge transitivity upon the gap debris in precision electro-discharge machining. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 68: 127-131.
- [21] Mohri, N. 1985. Mirror-like finishing by EDM. in: Proceedings of the 25th International Symposium on Machine Tool Design and Research: 329-336.
- [22] Mohri, N., Tsukamoto, J., Fujino, M. and 1985. Mirror-like finishing by EDM. in: Proceedings of the 25th International Symposium on Machine Tool Design and Research: 329-336.
- [23] Mohri, N., Tsukamoto, J., and Fujino, M. 1988. Surface modification by EDM-an innovation in EDM with semi-conductive electrodes. in: Proceedings of Winter Annual Meet ASME, 34: 21-30.
- [24] Mohri, N., Saito, N., and Higashi, M. A. 1991. A new process of finish machining on free surface by EDM methods. CIRP Annals - Manufacturing Technology, 40, 1: 207-210.
- [25] Montgomery, D. C. 1997. Design and Analysis of Experiments. fourth ed., Wiley, New York.
- [26] Narumiya, H. 1989. EDM by powder suspended working fluid, in: Proceedings of the 9th ISEM, 5-8.
- [27] Narumiya, H., Mohri, N., Saito, N., Otake, H., Tsnekawa, Y., Takawashi, T., and Kobayashi, K., 1989. EDM by pow-der suspended working fluid, in: Proceedings of 9th ISEM, 5-8.
- [28] Okada, A., Uno, Y., Hirao, K. 2000. Formation of hard layer by EDM with carbon powder mixed fluid using titanium electrode, in: Proceedings of 5th International Conference on Progress of Machining Technology, 464-469.
- [29] Simao, J. 2003. Work piece surface modification using electrical discharge machining, International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, 43: 121-128.
- [30] Peças, P. and Henriques,E. 2008. Effect of the powder concentration and dielectric flow in the surface morphology in electrical discharge machining with powder-mixed dielectric (PMD-EDM). Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 37: 1120-1132.
- [31] Pecas, P. and Henriques, E. A. 2003. Influence of silicon powder mixed dielectric on conventional electrical discharge machining. International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, 43: 1465- 1471.
- [32] Peças, P. and Henriques, E. 2008. Electrical discharge machining using simple and powder-mixed dielectric: The effect of the electrode area in the surface roughness and topography. Journal of materials processing technology, 200: 250-258.
- [33] Tzeng, F. Y. and Chen, F. 2003. A simple approach for robust design of high speed electrical-discharge machining technology. International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, 43, 217-227.
- [34] Tzeng, Y. F. and Lee, C. Y. 2001 Effects of powder characteristics on electro discharge machining efficiency. Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 17, 586-592.
- [35] Uno, Y. and Okada, A. 1997. Surface generation mechanism in electrical discharge machining with silicon powder mixed fluid. International Journal of Electrical Machining, 2, 13-18.
- [36] Uno, Y., Okada, A., Hayashi, Y., and Tabuchi, Y. 1998. Surface integrity in EDM of aluminum bronze with nickel powder mixed fluid. Journal of the Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers, 32, 70: 24-31 (in Japanese).
- [37] Wang, C. H., Lin, Y. C., Yan, B. H., and Huang, F. Y. 2001. Effect of characteristics of added powder on electrical discharge machining. Journal of Japan Institute of Light Metals, 42, 12: 2597-2604.
- [38] Wong, Y. S., Lim, L. C., Rahuman, I., and Tee, W. M. 1998. Near-mirror-finish phenomenon in EDM using powder-mixed dielectric. Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 79: 30-40.
- [39] Wu, K. L., Yan, B. H., Huang, F. Y., and Chen, S. C. 2005. Improvement of surface finish on SKD steel using electro-discharge machining with aluminum and surfactant added dielectric. Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, 45: 1195-1201.
- [40] Yan, B. H., Lin, Y. C., Huang, F. Y., and Wang, C. H. 2004. Surface modification of SKD 61 during EDM with metal powder in the dielectric. Materials Transactions, 42, 12: 2597-2604.
- [41] Yan, B. H. and Chen, S. L. 1993. Effects of dielectric with suspended aluminum powder on EDM, Journal of the Chinese Society Mechanical Engineers, 14, 3: 307-312.
- [42] Yan, B. H. and Chen, S. L. 1994. Characteristics of SKD11 by complex process of electric discharge machining using liquid suspended with aluminum powder. Journal of Japan Institute of Light Metals, 58, 9: 1067-1072.
- [43] Yan, B. H. and Chen, S. L. 1994. Effect of ultrasonic vibration on electrical discharge machining characteristics of Ti–6Al–4V alloy. Journal of Japan Institute of Light Metals, 44, 5: 281-285.
- [44] Zhao, W. S., Meng, Q. G., and Wang, Z. L. 2002. The application of research on powder mixed EDM in rough machining”, Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 129: 30-33.