Helsin Wang1, Keng-Tsang Hsu2, Chih-Hsin Hu1, Chih-Hsien Hsieh3, Ying-Tzu Ke2* 1 HCK Geophysical, Roosevelt Road, Taipei 106012, Taiwan 2 Department of Civil and Construction Engineering, Chaoyang University of Technology, Wufeng District, Taichung, 413310, Taiwan 3 Sinotech Construction Corporation, Ltd., Nanking East Road, Taipei 105409, Taiwan
Download Citation:
|
Download PDF
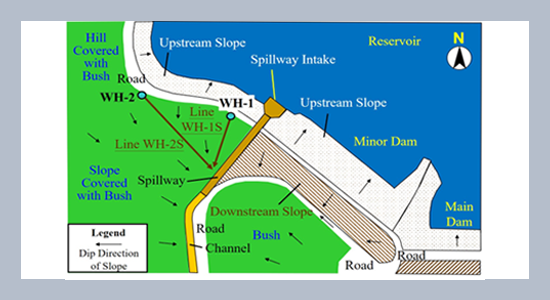
The electrical resistivity tomography technique is a geophysical inspection method widely used for several investigations, such as mining exploration, fault localization, groundwater flow, geological exploration, and pollution zones. Infusing brine into substructure can increase conductivity and becomes a useful medium to trace the path of the seepage flowing in rockfill dams. In this article, an elapsed-time electrical resistivity tomography technique was developed to monitor the potential seepage in the damaged dam slopes nearby a concrete spillway. Tracing the downhole brine seepage could effectively identify the possible direction and path of the seepage flowing through the rockfill dam mass in a few hours. The spatial distribution variations of electrical resistivity tomography images can also provide information about the potential sliding surface and the accumulation zones of the seepage in the downstream side slope of the dam.ABSTRACT
Keywords:
Electrical resistivity tomography, Brine seepage tracing, Elapsed-time, Slope failure, Groundwater, Dam.
Share this article with your colleagues
REFERENCES
ARTICLE INFORMATION
Received:
2022-11-21
Revised:
2023-01-04
Accepted:
2023-01-09
Available Online:
2023-02-15
Wang, H., Hsu, K.-T., Hu, C.-H., Hsieh, C.-H., Ke, Y.-T. Brine seepage tracing in a damaged dam slope using elapsed-time electrical resistivity tomography. International Journal of Applied Science and Engineering, 20, 2022300. https://doi.org/10.6703/IJASE.202303_20(1).010
Cite this article:
Copyright The Author(s). This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY 4.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are cited.