Chih-Hung Chiang1,2*, Hung-Yu Tao1, Yung-Chiang Lin1 1 Center for Non-destructive Testing, Chaoyang University of Technology
2 Department of Aeronautical Engineering, Chaoyang University of Technology, Wufeng District, Taichung, Taiwan
Download Citation:
|
Download PDF
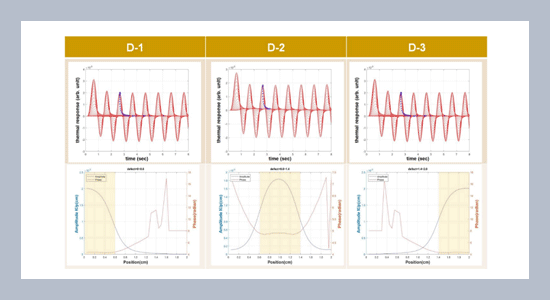
The transient heat transfer within a layered structure can be modeled efficiently using the thermal quadrupole methods. Such numerical simulations would contribute to effective experimental design for thermography inspection applications of composite materials. Current research is part of such effort that focuses on the parametric study on both a two-layer model and a four-layer model. The variation of amplitude curves agrees with the lateral position of the interfacial discontinuity in general. The sudden increase in the phase value distinctively indicates the end point of the same discontinuity. Hence the lateral location of an embedded interfacial discontinuity can be readily identified from the Laplace surface temperature. The layer thickness does not have significant effect on the general trend observed in the parametric analysis presented in this work. The advantage of the numerical modeling of layered structures using thermal quadrupoles lies in that thermal quadrupoles can be easily extended to multiple layers containing internal anomaly between different layers.ABSTRACT
Keywords:
Passive thermography, Thermal quadrupoles, Layered media, Fiber reinforced polymer composites.
Share this article with your colleagues
REFERENCES
ARTICLE INFORMATION
Received:
2020-11-30
Revised:
2021-03-08
Accepted:
2021-03-08
Available Online:
2021-06-01
Chiang, C.-H., Tao, H.-Y., Lin, Y.-C. 2021. Transient thermal analysis of layered media based on thermal quadrupoles, International Journal of Applied Science and Engineering, 18, 2020312. https://doi.org/10.6703/IJASE.202106_18(3).001
Cite this article:
Copyright The Author(s). This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY 4.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are cited.