Chen-Chu Lai1, Xinran Zhou2, Hao-Kuang Wang3,4, Ying-Chao Lin5,6,7, Hui-Yi Lin8, Tzong-Der Way2,9, Bing-Lan Liu1* 1 Department of Applied Chemistry, Chaoyang University of Technology, Taichung, Taiwan, ROC 2 Department of Biological Science and Technology, College of Life Sciences, China Medical University, Taichung, Taiwan, ROC 3 Department of Neurosurgery, E-Da Hospital/I-Shou University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan, ROC 4 School of Medicine, I-Shou University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan, ROC 5 Division of Neurosurgery, Buddhist Tzu Chi General Hospital, Taichung Branch, Taiwan 6 School of Medicine, Tzu Chi University, Hualien, Taiwan, ROC 7 Department of Medical Imaging and Radiological Science, Central Taiwan University of Science and Technology, Taichung, Taiwan, ROC 8 School of Pharmacy, College of Medicine, College of Pharmacy, China Medical University, Taichung, Taiwan, ROC 9 Department of Health and Nutrition Biotechnology, Asia University, Taichung, Taiwan, ROC.
Download Citation:
|
Download PDF
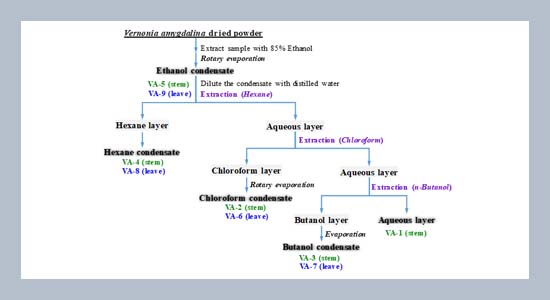
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is more common around the world and due to multiple hepatocarcinogenic causes, it is imperative to find drugs that can alleviate the worsening of liver disease or inhibit the occurrence of liver cancer. Recent studies found that Vernonia amygdalina (VA) extracts exhibited the anti-cancer ability, including breast, prostate and nasopharynx cancer. Moreover, recent experiments showed that VA extract has the potential to be hepatoprotective, antioxidant, and antifibrotic to the liver. In this study, the anti-cancer effects and its possible mechanisms of VA extracts in human hepatoma cancer Hep 3B cells were investigated. Western blot, flow cytometry, and cell migration and invasion assays were used to explore the anticancer effects of VA extracts against HCC cells. The MTT assay revealed that the chloroform-leave extract of VA (VA-6) exhibited the most potent ability to inhibit the proliferation of Hep 3B cells than other extracts. Flow cytometric analysis found that VA-6 induced apoptosis in Hep 3B cells. Western blotting demonstrated VA-6 induced apoptosis through the inhibition of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. The results showed that cancer migration and invasion could be repressed by VA-6 through the inhibition of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). Interestingly, we found that VA-6 enhanced the sensitivity of paclitaxel and doxorubicin to Hep 3B cell growth.ABSTRACT
Keywords:
Hepatocellular carcinoma, Vernonia amygdalina, Epithelial-mesenchymal transition, Apoptosis.
Share this article with your colleagues
REFERENCES
ARTICLE INFORMATION
Received:
2021-03-17
Revised:
2021-11-02
Accepted:
2021-11-03
Available Online:
2022-03-01
Lai, C.-C., Xinran Zhou, Hao-Kuang Wang, Ying-Chao Lin, Hui-Yi Lin, Tzong-Der Way, Bing-Lan Liu, Vernonia amygdalina extract induces apoptosis and inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition in Hep 3B cells through the inhibition of PI3k/Akt signaling pathway. International Journal of Applied Science and Engineering, 19, 2021086. https://doi.org/10.6703/IJASE.202203_19(1).002
Cite this article:
Copyright The Author(s). This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY 4.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are cited.