Qutaiba I. Ali* Computer Engineering Department/Mosul University/IRAQ
Download Citation:
|
Download PDF
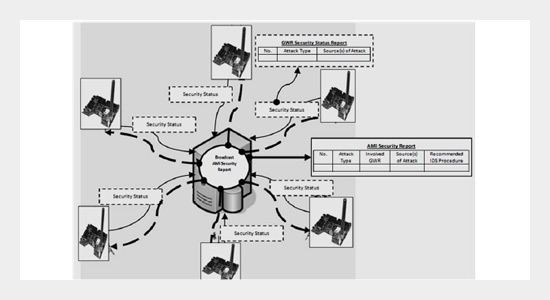
This paper deals with the design issues of a secure and green Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI). The first part of the paper suggests enhancing the reliability of AMI system using wireless ad hoc Network technology. The suggested Advanced Metering Infrastructure consists of various types of wireless nodes we called Green Wireless Router (GWR). Here, we propose that GWRs can harvest the energy needed for its work from the surrounding environment, especially solar energy. Such suggestion permits to install GWRs in any place without considering the power supply availability and hence, extensive area is covered by the AMI. The different network traffic patterns generated from running a customized AMI simulation model were used in an experimental network based mainly on UBICOM IP2022 network processor platform (as the implementation of the intended GWR)with the aim of measuring its power consumption under different realistic circumstances. In order to decrease the power consumption of the suggested GWR and to extend the life time of the batteries, a two power management schemes we called Controlled Duty Cycling(CDC) and Event Driven Duty Cycling were suggested and implemented. The second part of the paper suggests a GWR security model to protect it against different internal and external threats. The suggested GWR security model must respond to many objectives, it should ensure that the administrative information exchanged is correct and undiscoverable (information authenticity and privacy), the source is who he claims to be (message integrity and source authentication) and the system is robust and available (using Cooperative Intrusion Detection System).ABSTRACT
Keywords:
Advanced Metering Infrastructure(AMI), Green Wireless Router (GWR), Solar Energy Harvesting, Network Security.
Share this article with your colleagues
[1] Kolhe M., 2012, “Smart Grid: Charting a New Energy Future: Research Development and Demonstration”, The Electricity Journal, vol. 25, issue 2, pp. 88-93.REFERENCES
[2] Wang W., Xu Y. , Khanna M., 2011, “A survey on the communication architectures in smart grid” Elsevier’s Computer Networks Journal, vol55, issue 15, pp 3604–3629.
[3] Gungor V. , Sahin D., Kocak T., Ergut S., Buccella C., Cecati C., and Hancke G., 2011. “Smart grid technologies: Communication technologies and standards,” IEEE Trans. Ind. Informat., vol. 7, no. 4, pp. 529–539.
[4] Hamlyn A., 2008, “Computer Network Security Management and Authentication of Smart Grids Operations,” IEEE Power and Energy Society General Meeting — Conversion and Delivery of Electrical Energy in the 21st Century, 2008.
[5] Ayday E. and Rajagopal S., 2011, “Secure, Intuitive and low-Cost Device Authentication for Smart Grid Networks,” IEEE Consumer Commun. And Net. Conf., pp. 1161–65.
[6] Khurana H., 2010, “Design Principles for Power Grid Cyber-Infrastructure Authentication Protocols,” 43rd Hawaii Int’l. Conf. Sys. Sciences, pp. 1–10.
[7] Efthymiou C. and Kalogridis G., 2010, “Smart Grid Privacy via Anonymization of Smart Metering Data,” IEEE SmartGridComm ’10, pp. 238–43.
[8] Wicker S. and Thomas R., 2011, “A Privacy-Aware Architecture for Demand Response Systems,” 44th Hawaii Int’l. Conf. Sys. Sciences, pp. 1–9.
[9] Mehra T., Dehalwar V., Kolhe M., 2013, “Data Communication Security of Advanced Metering Infrastructure in Smart Grid:, 5th International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Communication Networks.
[10] Yan Y., Qingyang Hu R., Das S., Sharif H. and Qian Y., 2013, “An Efficient Security Protocol for Advanced Metering Infrastructure in Smart Grid”, IEEE Network.
[11] Bartoli A., Hernandez-Serrano J., Soriano M., Dohler M., Kountouris A., Barthel D., 2010, “Secure Lossless Aggregation for Smart Grid M2M Networks”, First IEEE International conference on Smart Grid Communications, pp 333-338.
[12] Madava D., Fafoutis X., Andersen C., Dragoni N., 2013, " Medium Access Control for Thermal Energy Harvesting in Advanced Metering Infrastructures", EuroCon 2013, Zagreb, Croatia.
[13] Tan O., G¨und¨uz D., and Poor H., 2013, “Increasing Smart Meter Privacy Through Energy Harvesting and Storage Devices”, IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, VOL. 31, NO. 7,.
[14] Ali Q., 2011, " Design & Implementation of a Mobile Phone Charging System Based on Solar Energy Harvesting", IJEEE Journal, Vol.7, No.1, available at : http://www.ijeee.org/volums/volume7/IJEEE7PDF/Paper713.pdf.
[15] IP2022 Ubicom Data Sheet, WWW.Ubicom.com.
[16] Ali Q., Faher F., 2013, "Evaluation of Routing Protocols of Wireless ad hoc for AMI Systems Using OPNET Simulator", 2nd Scientific & Engineering Conference.
[17] Luiz D., Dasilva A., Tao l., Scott D. , Midkiff F., 2004, “Mobile Ad-hoc Network Routing Protocols: Methodologies and Applications”, ECE Department, Virginia Tech.
[18] Anastasi G., Conti M., Francesco M., Passarella A., 2009, " Energy conservation in wireless sensor networks: A survey", Elsevier ad hoc Networks Journal , vol.7 pp537–568.
[19] Ali Q., Lazim S., Fathi E., 2012, “Securing Wireless Sensor Network (WSN) Using Embedded Intrusion Detection Systems”, IJEEE Journal, Vol.8 No.1.
[20] Ali Q., Lazim S., 2012, "Design & Implementation of an embedded Intrusion Detection System for Wireless Applications", IET Information Security Journal, Vol.6, Issue 3.
[21] Erritali M, El Ouahidi B., 2013, "A Survey on AMI Intrusion Detection Systems", Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference on Systems, Control, Signal Processing and Informatics.
ARTICLE INFORMATION
Received:
2015-09-19
Revised:
2016-01-18
Accepted:
2017-02-25
Available Online:
2017-02-01
Ali, Q.I. 2017. Towards secure & green advanced metering infrastructure (AMI). International Journal of Applied Science and Engineering, 14, 147–169. https://doi.org/10.6703/IJASE.2017.14(3).147
Cite this article: